Hydrostatic Test Rig Design Drawings for CGA C1 and IDEST compliant cylinder testing
Below is presented the working drawings of a simple hydrostatic rig design, that with traceable calibrated gauges, correct installation, trained operators working in accordance with the standards can achieve measurement accuracy sufficient to meet International standards used for testing compressed gas cylinders such as those written by DOT/CFR/CGA, BS, EN, ISO etc
Click on any picture to download a full size high resolution picture full size picture
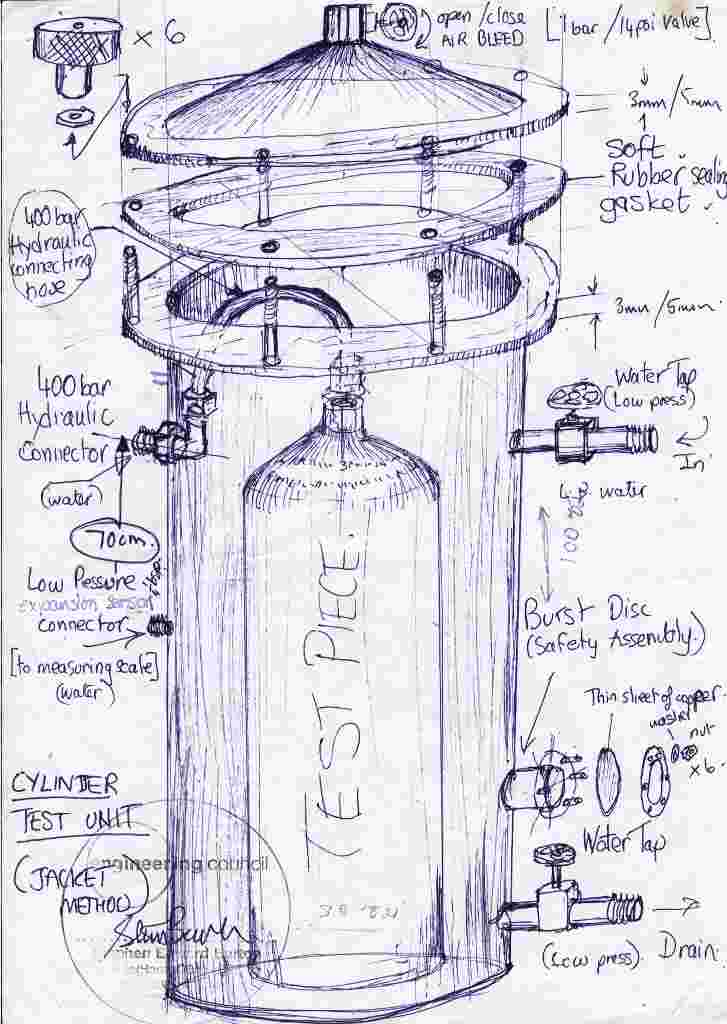
Main Cylinder Jacket connections

Test Bench Layout |
Overhead Pulley arrangement |
Main Pressure measurement manifold |
10,000psi Madam Air powered water pump |
Cylinder expansion burrette |
Custom Hydraulic pipes |
The worlds major cylinder hydrostatic test equipment including fully automated manufacturers are:
An example of the air powered Low volume high pressure water pumps used in these test systems is:-
The hydrostatic test system represents the largest capital equipment expenditure of the fledging test center.
Expensive fully automated systems capable of testing a hundred cylinders per day and costing $100,000 + are not required by everyone. However, a manual system capable of hydro-testing a few tens of cylinders a day can be locally manufactured relatively easily by any workshop with basic engineering and welding facilities for a few thousand dollars (including hydraulic pump,
hoses and gauges)
The American Compressed Gas Association standard for hydro-static testing of high pressure cylinders CGA C1
CGA C-1 ” Methods for Hydrostatic Testing of Compressed Gas Cylinders” contains a full specification & description of the system components..
Anyone considering building a hydrotest system should obtain a copy of this standard first. This method can be considered as the gold standard for conducting hydro-static testing. Any company that has a CGA C1 compliant system can rest easy that their system can easily test cylinders to any other country’s hydro-static test standard.
Note that the CFR/DOT/CGA rules for conducting hydro-static tests of high pressure cylinders requires that the jacket method is used – a proof test alone (such as is permitted in Europe) is considered woefully inadequate, since it does not discover any permanent distortion created by pressurizing the cylinder to the hydro-static test pressure, and is thus NOT acceptable.
CGA C1 calls for such things as:-
- NIST Traceable calibrated pressure gauge manufactured to better than +/-0.5% accuracy, and calibrated to better than +/-1%
- NIST Traceable calibrated burrete or other expansion measurement system with full range accuracy of better than +/-0.5%
- An example expansion measurement system could be a digital weighing scale to measurement water displacement, since 1.0 cc of water weighs 1.0 gram
- NIST Traceable calibrated cylinder with its expansion known to better than +/1% throughout the range of test pressures.
- This cylinder would typically be re-calibrated every 5 years – usually just prior to the DOT re-audit of the facility.
- A daily system check that the hydro-test apparatus gives Elastic Expansion results within +/-1% of the calibrated cylinders certified value throughout the range of pressures used.
- The visual and hydro-static inspection results caried out in accordance with CGA C1, C6, C6.1 as given below:-
- Daily system calibration check form
- Visual Inspection data collection form
- Hydro-static inspection data collection form
Common hydro-static inspection terms used:-
TE = Total Expansion
EE = Elastic Expansion
PE = Permanent Expansion
REE= Rejection elastic Expansion; The maximum permitted EE the cylinder is allowed to exhibit (sometimes marked in cc on the shoulder of cylinders)
Manual Cylinder hydro-testing in the Zanzibar, Africa
(cylinders that do not pass VIP or Hydro-testing for whatever reason have to be exploded in order to convince the natives that the cylinder really is no good anymore…)
Singapore Hydro Rig – Manufactured by Portly Products Co










